Measuring green-product moisture
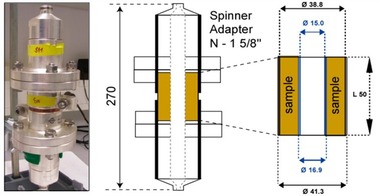
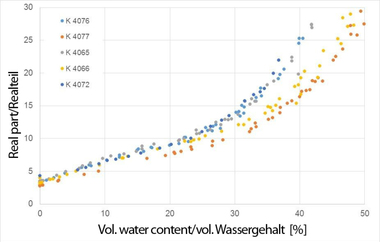
All regular-market measuring systems determine the water content of a given medium by indirect means, i.e., by exploiting a certain physical effect. The consequences of a change in moisture content affect the factor in question, giving rise to a corresponding, parallel change in the signal arriving from the sensor. In the absence of an absolute scale of indication, the measuring probe has to be calibrated for the specific material in question.
The measuring principle is based on the capacitive high-frequency approach in which the difference between the dielectric constants of water (ε = 80) and of the material of interest is analysed. Most materials have a dielectric constant situated within the range ε = 3…10. The water content of the material yields a broad band of evaluable dielectric constants, so high resolution is obtainable for the high-frequency capacitive field in question. The electronic probe then further processes the obtained signal and outputs the result as the sought measuring signal. Consequently, this implies that the probe has to be recalibrated for each different material, and a material-specific calibration curve is required for evaluating the signal being picked off of the probe.
Dr.-Ing. Anne Tretau, Institut für Ziegelforschung Essen e. V.