Energy-conserving options for the
brick shaping process
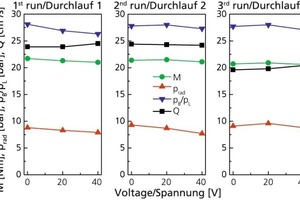
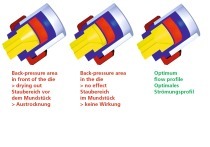
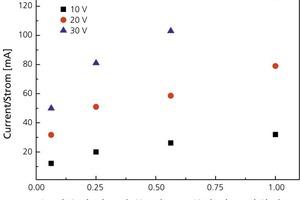
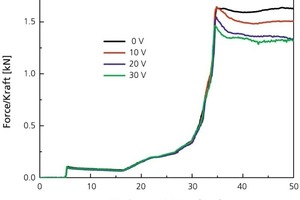
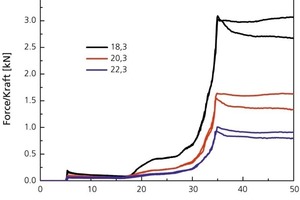
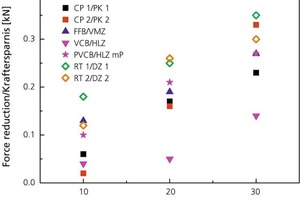
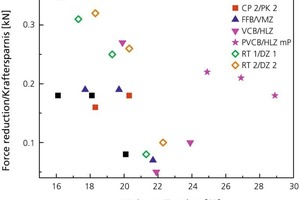
The present contribution investigates electroosmotic means of reducing wall friction in auger extruders. The objective was to reduce body moisture and, hence, the drying energy requirement, i.e., to decrease the power consumption of the extruder. A piston press with core die and appropriately arranged electrodes was constructed to enable investigation and quantification of this effect. While this did reduce the extrusion force requirement for all test batches, the plastic roof tile clays yielded somewhat superior results in comparison with the nonplastic shale clays.
1 Introduction
Considering that the brick and tile industry counts among the more energy intensive sectors and that the cost of energy accounts for a very large share of the end products‘ overall cost, any new progress made in reducing the consumption of energy is of major significance. The purpose of the subject research project was to establish the extent to which reduced wall friction within the extruder would allow corresponding reductions in body moisture and, hence, the drying energy requirement or power consumption of the extruder.
2 Scientific principles
The electroosmotic-flow...

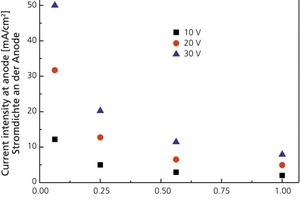
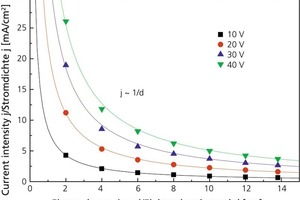

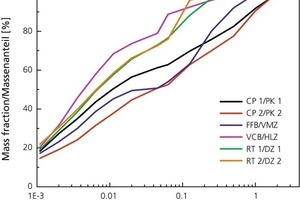
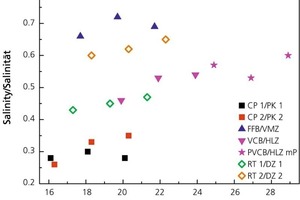
![»8 Die-element dimensions on laboratory extruder [mm]](https://www.zi-online.info/imgs/tok_98fc7d4d19105a531eb3c6a09d4e20dc/w300_h200_x329_y146_101483454_df1ad8a74d.jpg)