Avoidance of damage due to strength-reducing reactions in the preheating zone of tunnel kilns
1 Objective
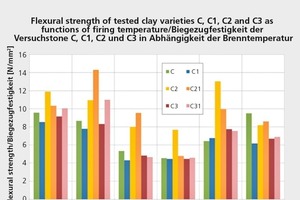
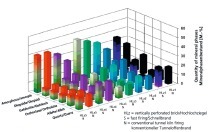
Decomposition and transformation reactions taking place at temperatures between 500 and 800° C (900° C) provoke a loss of strength in brick green bodies. The purpose of these investigations, therefore, was to counteract such losses by means of raw-material measures and the use of inorganic binders of a type already employed in the refractories industry.
2 Background
Fluctuating temperatures and corresponding differences in expansion and shrinkage can cause stress-induced cracking. This can be countered by improving the stress tolerance of the nascent body.
3 Experimental procedure
This...