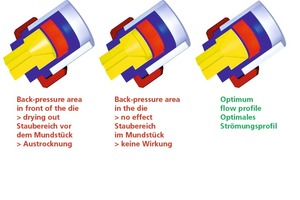
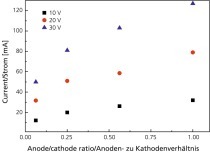
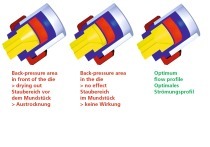
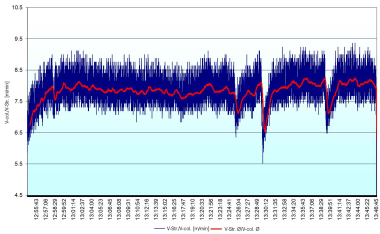
The paper examines the possibility of reducing wall friction in the die of an extruder by means of electro-osmosis. For this purpose, electric voltage is applied between the die, which functions as a cathode, and an anode inside the extruder. As a result of this set-up, a film of water is formed between the clay and the die, reducing wall friction. In the scope of a research project, it was investigated whether this process is suitable to reduce the moisture content of a clay body required for extrusion and accordingly lower the consumption of drying energy or alternatively the power...