Influence of the pH value on the plasticity of clay bodies for bricks
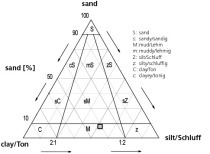
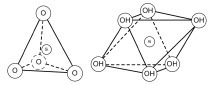
The findings of a study on the active principles and effects of a change in the pH value with regard to shaping, drying and firing behaviour as well as the leachability of heavy metals in the product are discussed The natural souring process was artificially replicated by means of the addition of acid residues. The reason for this is an improved clay disintegration during the souring process, which can be attributed to the formation of acid decomposition products. Improved clay disintegration leads to an increase in plasticity. From these results a saving of energy in the shaping and drying processes as well as improved product quality. The increase in plasticity in the acid range is caused by the changing interaction of the clay minerals. This results in a change in the surface charges, which leads to increased formation of a house of cards structure. In addition, the achieved body/brick properties are compared as a function of different storage times and the possibilities for selection of the residues used for the brick product are examined more closely.
B.eng. Daniel Schnabel, Institut für Ziegelforschung Essen e.V.