Sensor-assisted sorting process for recycling construction materials
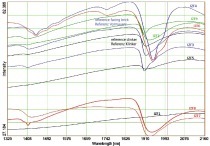
Returning used masonry bricks to the production cycle and, likewise, closing resource recycling loops both require that the material be mono-fractionated. That, in turn, requires that the bricks be separated from masonry rubble by extraction processes and from plaster and other extraneous/waste material by automatic sorting processes situated downstream. Sensor-assisted sorting in the near-infrared range is helpful in separating gypsum-based plaster and similar construction materials from demolished brick masonry. Near-infrared sortation is a non-destructive, near-surface process in which spectra containing information about the chemical-mineralogical composition are obtained. Chemometric methods enable the use of such spectra for differentiating between diverse building materials and, hence, recovering segregated volumes of them.
Dipl.-Ing. Mirko Landmann, IAB – Institut für Angewandte Bauforschung Weimar gemeinnützige GmbH
Leonard Raumann, M.Sc., Institut für Ziegelforschung Essen e.V.