Product development based on broken bricks
The Sutracrete project, funded by the BMBF, enables the reuse of masonry rubble in concrete products. It integrates brick dust as a pozzolanic additive and brick aggregate as a sand substitute to combat resource scarcity and promote the circular economy. Traditional brick production consumes large amounts of sand and clay – Sutracrete reduces this consumption by up to 30%, protects ecosystems and lowers CO2 emissions.
The durability of the modified materials was tested using dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA): The results show improved resistance to thermal and mechanical stress, with reduced cracking and longer service life. The sand substitute has a particular impact on resource consumption: brick dust replaces cement components, while the coarser aggregate substitutes sand.
A highlight is the fluorescence marker for traceability: TrackByStars enables the tamper-proof labelling of products using randomly distributed fluorescent particles that form a unique, three-dimensional fingerprint pattern – invisible until activated by special light. It supports lifelong traceability and sorting of materials, especially in recycling, and serves as the basis for digital product passports.
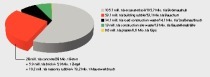
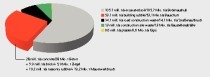
The life cycle assessment highlights the advantage: the life cycle analysis was applied to mineral construction waste (one third of waste in the UK/EU) in order to process heterogeneous brick and masonry waste as secondary raw materials. This allows a defined proportion of recycled material to be used in the cement and concrete industry, increasing the recycling rate.