Causes and avoidance of firing-related damage
Part 2: Strength-reducing reactions in the heating-up zone from 500 to 800° C
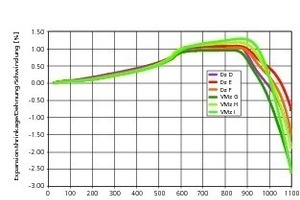
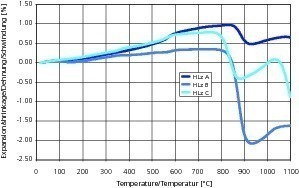
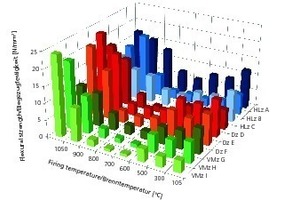
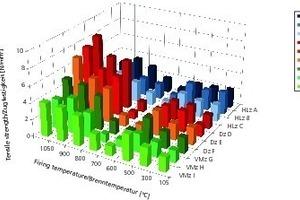
Part 1 of this contribution dealt with diffusion-dependent reactions in the heating-up zone at ≤ 500° C (Zi Brick and Tile Industry International 11/2013). Now, Part 2 looks into the firing of bricks in the temperature range 500 to 800° C. Expansion and, to some extent, shrinkage processes take place within that range of temperatures. Solid-state reactions with strength-reducing effects on the freshly forming body also occur within that same range.