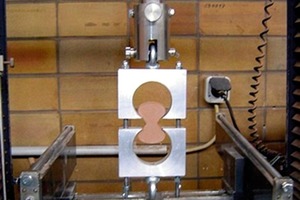
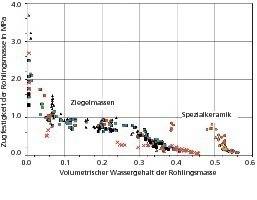
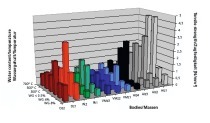
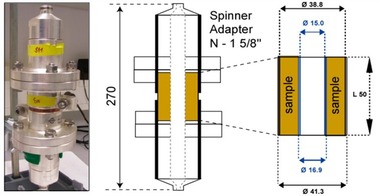
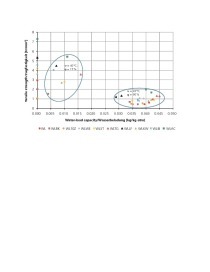
Influence of the inner surface of drying green ceramic products on their moisture-dependent tensile strength
Test results relating to the moisture-dependent tearing strength of green brick products are described. A detailed presentation of these relations will be included in the Zi Annual 2010. This also takes into account the strength development in the first drying section and the partly extreme strength increase which is attainable with very high dryness, but which unfortunately falls back again to the base values under “normal” atmospheres.
1 Introduction
The determination of the pore size distribution by means of mercury penetration porosimetry leads as a secondary result to the specific pore surface a (total pore area) of the dry specimen. This is given mostly in m²/g and for clayey and other mineral materials is equal to the mass-specific free particle surface.
As described in greater detail in [1], for clay particles in normal moist atmospheres these surfaces are always completely covered by thin water sheaths, which merge into each other at the contact points between individual mineral particles.
Consequently the water...