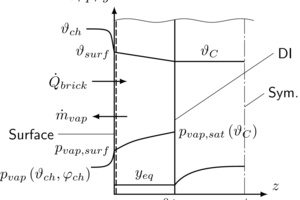
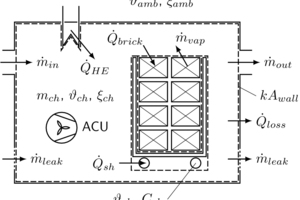
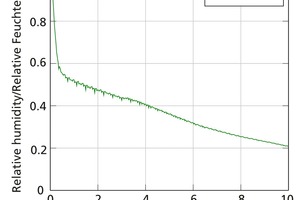
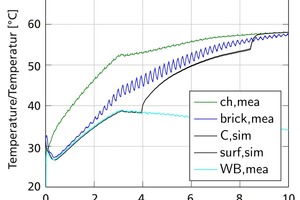
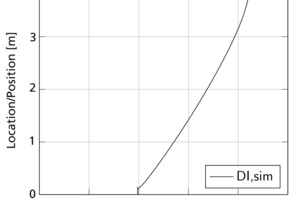
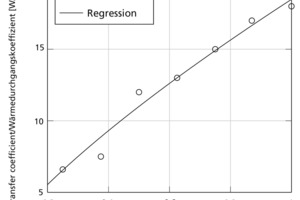
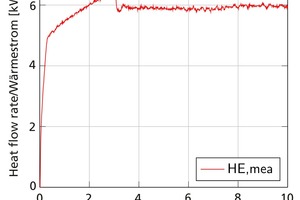
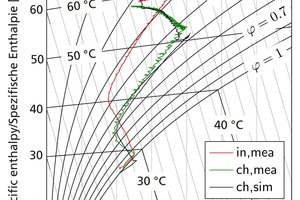
Modelling, simulation and validation of brick drying in a laboratory chamber dryer
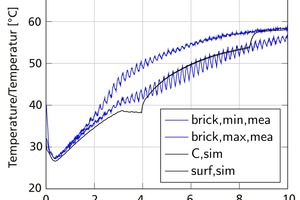
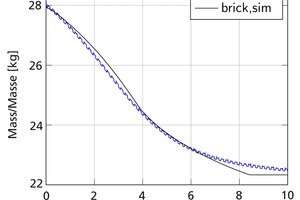
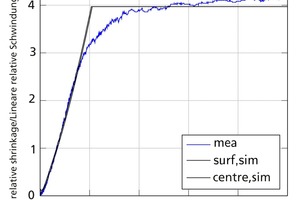
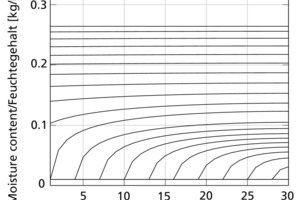
This article describes the development of an open, easily expandable drying library for use in investigating the drying behaviour of clay bricks in a chamber dryer. The proposed modelling approaches and resultant mathematical formulations were implemented in the modelling language Modelica and validated as a specific application on the basis of measured data from drying tests performed in a laboratory container. All key properties and processes were reproduced with sufficient accuracy. Multi-domain simulations, such as optimization tasks in connection with plant management or performance studies, are easily accomplished by combining elements of the drying library with other user-defined or standard libraries.
1 Introduction
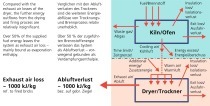
Convective drying is a very energy intensive process, because the latent evaporation enthalpy required for removing the entire moisture content must be supplied. Also, convective dryers exhibit notoriously low efficiency, often below 50% [1].
However, the use of dryers is on the increase, due not least to the market appearance of numerous new drying-relevant appurtenances. In 2016, the industry accounted for approx. 30% of Austria’s end-use energy consumption. It counts among the main sources of climate-relevant emissions, since only 50% of the overall industrial energy...